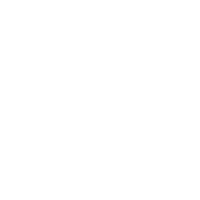
Leader: PhD Agnieszka Nawrocka
Team: Assoc. Prof. DSc Antoni Miś; Assoc. Prof. DSc Robert Rusinek; PhD Marek Gancarz; Zbigniew Niewiadomski; MSc Magdalena Krekora
Nowadays, consumers demand dietary fibre-enriched products of appropriate taste, texture, smell and appearance as a result of growing consumers’ awareness concerning health benefits of the consumption of this kinds of products. Wheat bread is a major source of energy in the western diet, and thus an adequate carrier to deliver nutritionally valuable compounds such as dietary fibre and antioxidants. However, addition of dietary fibre preparations to wheat bread significantly reduces its quality, for example: decrease in loaf volume, gritty texture, and unsuitable taste and smell (Collar et al., 2007). The bread quality is strictly related to the structure of gluten proteins (gliadins and glutenins), which participate in formation of a continuous viscoelastic gluten network within dough. Addition of different chemical compounds (e.g. water-soluble and water-insoluble polysaccharides, anthocyanins and phenolic acids) to the bread dough disturbs the gluten network by creating new hydrogen bonds and causing changes in disulphide bridges conformation. It leads to abnormal folding or aggregation of protein complexes and results in the formation of a gluten network characterized by different mechanical properties.
The research task achieves the following scientific aims:
- Determination of changes in the secondary and tertiary structure of gluten proteins induced by particular compounds of dietary fibre preparations (polysaccharides, polyphenols and tocopherols) and dehydratation.
- Determination of rheological effects caused by dehydratation process during the dough kneading as a result of addition of the dietary fibre preparations.
- Determination how the dietary fibre preparations affects the wheat bread quality during its storage.